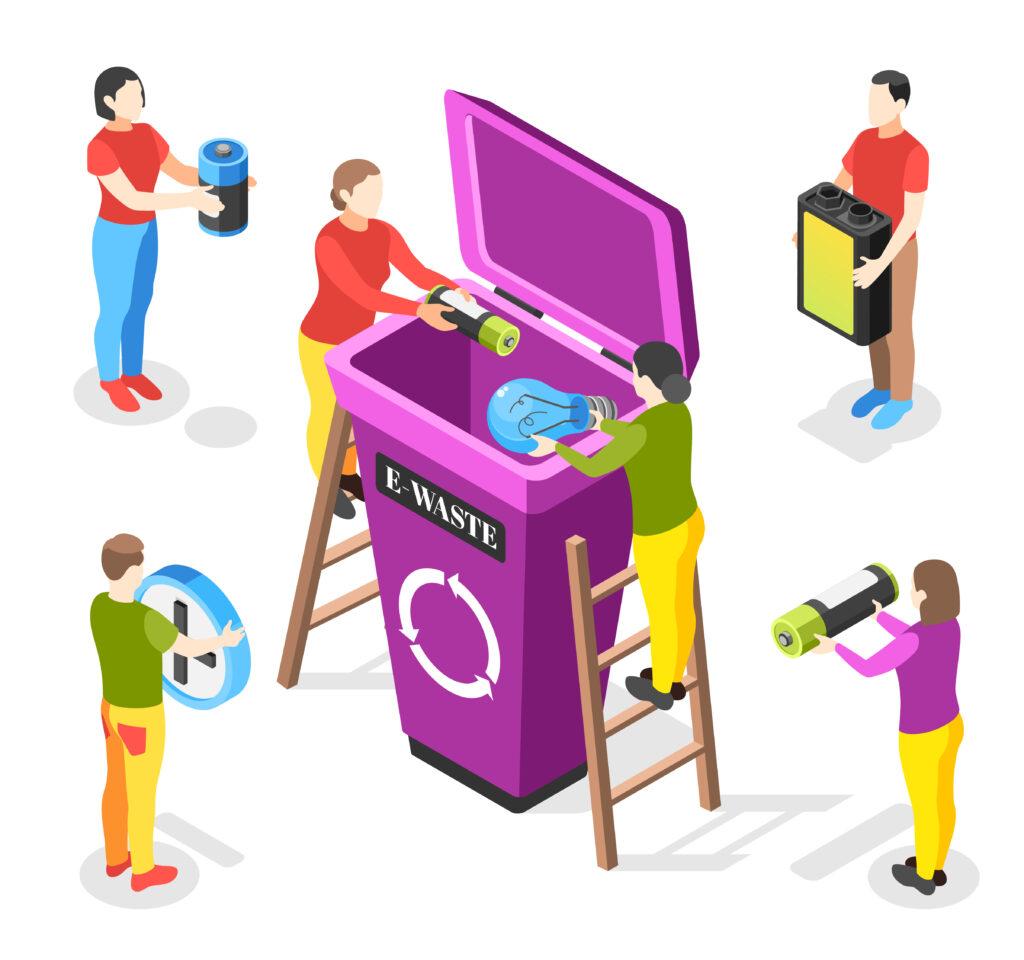
With the advancement of technology, E-waste has become a topic of growing concern. We generate 40 million tons of various types of E-waste every year, worldwide. It’s present all around us but more often than not we are completely oblivious to its presence. This is due to many reasons, primarily the lack of awareness about the diverse varieties of E-waste. In this blog, we’ll discuss the different types of E-waste present around us and also acknowledge the way to dispose of it safely. By the conclusion of this blog, you’ll find it astonishing to uncover the significant volume of electronic waste concealed within forgotten cardboard boxes and storage spaces in your home, all of which may have gone unnoticed.
Types of E-waste
1. Obsolete Electronics
There is no denial many of us still have our antiquated televisions and outdated computer systems kept in some forgotten corners of our houses. These devices serve absolutely no practical purpose yet we keep them hidden in our basements or storerooms unaware of the harm they pose to us. LCD desktop monitors, LCD televisions, Plasma Televisions, TVs, and old computers with Cathode Ray tubes are the most common hazardous electronic items. Regrettably, retaining these obsolete devices on our premises exposes us to various health risks.
2. Mobile Phones
According to a popular site “The World Counts” report on E-waste facts, an average cellphone user replaces their unit once every 18 months while an astonishing amount of 1 Billion cellphones go into production annually. With new smartphone models released so frequently, the question arises: What happens to these outdated and discarded cell phones? Unfortunately, many of them end up being disposed of improperly, either forgotten in storage warehouses or left to deteriorate in open landfills. These devices contain valuable metals and components that can be recycled if properly disposed of.
3. Batteries
Batteries from various devices such as laptops, cameras, and even car batteries are a major component of E-waste. Many batteries contain toxic or hazardous materials, such as heavy metals and corrosive acids. If not properly managed, these substances can leach into the soil and water, posing risks to human health and the environment. Some of the batteries like Lithium-ion batteries, in particular, can even catch fire if damaged, punctured, or exposed to high temperatures.
4. Household Appliances
According to a new report from the United Nations University, about 60 percent of electronic waste finds its origins in the realm of household appliances. Spanning from larger appliances like refrigerator and washing machines to small counterparts like microwaves, all of these domestic appliances contributes to a significant portion of E-waste once they reach the end of their operational lifespan.
These household essentials, which we often take for granted in our daily lives, collectively constitute a substantial portion of the ever-growing electronic waste crisis. Once these appliances cease to function or are deemed obsolete due to technological advancements, they venture down a path toward becoming electronic waste.
5. Gaming Consoles and E-toys
Given the surging popularity of the gaming consoles, there’s always a new edition of Xbox right around the corner. And we as a part of a consumer-driven society, always feel the need to be on the bandwagon to buy the latest editions. Consequently, the older consoles are moved to the sidelines, making way for their newer counterparts. These old consoles make their way to dump yards emitting toxins in the air.
An analogous narrative is observed with other forms of electronic entertainment, including video games, electric trains, and car racing sets. All of these gadgets make up a fair portion of E-waste and need to be disposed of responsively.
6. Medical Devices
As with any electronic equipment, medical devices can contribute to electronic waste (e-waste) when they reach the end of their lifecycle. Medical equipment, such as X-ray machines and MRI scanners, can become e-waste as hospitals and clinics upgrade their technology. These devices often contain complex electronic components and hazardous materials such as lead, mercury, and cadmium which can pollute the environment if not properly disposed of.
7. Cables and Chargers
With the widespread use of mobiles and laptops, there is a high demand for cables and charges. Being relatively small in size they are easy to misplace which calls for buying newer ones. Over time, cables, chargers, and adapters tend to accumulate in drawers. While they might seem insignificant, the sheer volume of these items contributes to e-waste.
What steps to take once you know your E-garbage?
E-waste Recycling!
Once you are aware of the E-waste present around you and the harm it poses to our bodies and the environment, you would be urged to dispose of it. However, disposing of it in open land will affect us and the environment even more seriously. Like other kachra, E-kachra if not disposed of properly can affect our environment negatively.
To know more about it you can read our blog on Improper E-waste Management: How it affects the environment.
E-waste comprises 70% of our overall toxic waste. Proper disposal of e-waste is of utmost importance to mitigate its adverse effects. Thankfully, there are numerous e-waste management companies in India actively working towards addressing this issue. These companies operate E-waste recycling plants in remote areas, ensuring the safe and secure disposal of all types of E-waste.
Conclusion
40 million tons of electronic waste produced every year poses a critical environmental challenge globally. Shockingly only 12.5% of this vast amount of E-Waste is recycled, exacerbating the issue at hand. It is essential to raise awareness about the various types of e-waste and promote responsible disposal practices. By taking proactive measures, we can strive towards a more sustainable future and create a greener world for generations to come.