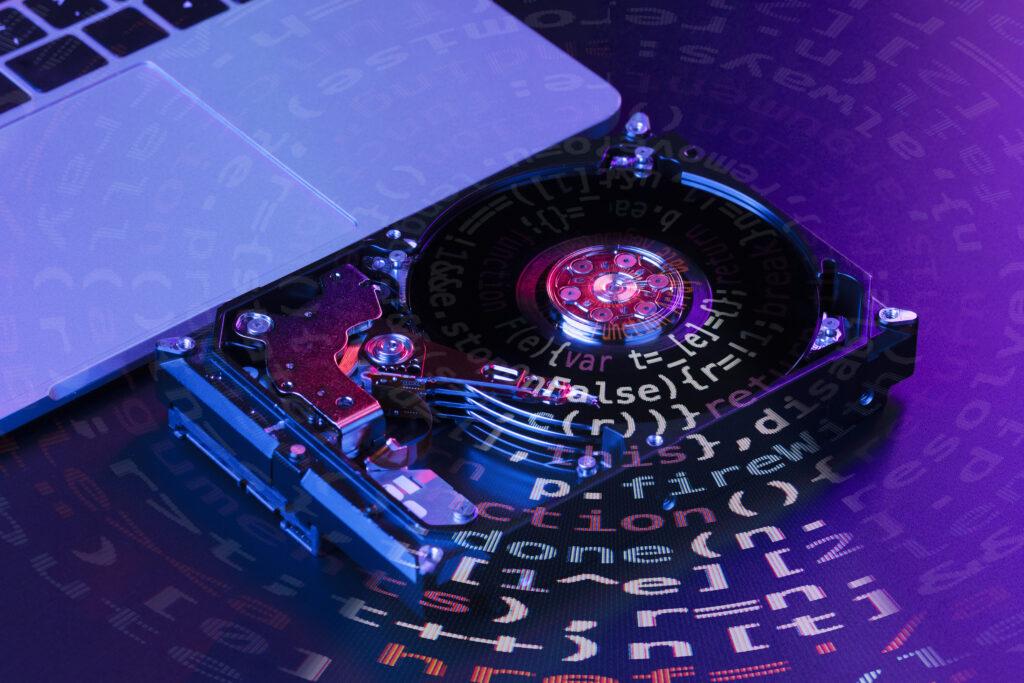
Our storage capacity is expanding rapidly to match the digital world’s growth while shrinking the physical size of storage devices. With our data volume continuously increasing, theft risks magnify across systems of all sizes. In the past, data theft for financial gain or sabotage might have involved stealing a large folder from a file cabinet. However, today, a portable gadget smaller than a candy bar can carry the equivalent of an entire records room or even a library’s worth of information. Employing Secure data destruction is a powerful defense against several problems brought on by such breaches.
Proper data maintenance and storage procedures constitute a portion of overall security. If the data is not secured or deleted, an unauthorized user could access a system from a distance or in person and steal or modify the data. Similarly, imagine a company updating its computer gear. Any old storage medium that the company has or improperly discarded runs the risk of being the subject of malicious “salvage” and henceforth should be properly disposed of by the competent agency.
What is Data Destruction?
Data destruction is a process for making digital data unreadable and unrecoverable. In essence, it is equivalent to data sanitization, which employs comparable techniques. However, it also entails confirming that the data has been securely erased.
Verification can be done with as little as a one-line document, but it is preferable to furnish full legal certificates from a data destruction company. As a result, a chain of custody and auditable trail are created, detailing the devices destroyed, the procedures employed, and other relevant information.
A corporation that offers data destruction services to your company will also perform verification and offer a variety of solutions, ranging from straightforward deletion to complete hard drive destruction.
What are different Data Destruction methods?
1. Formatting or Erasing
This is the most basic method of data destruction, but it does not delete data from storage media. Instead, erasure gets rid of digital references to the data, making it inaccessible to a computer or any other device reading the medium. Erasure is the least secure procedure, although it may be done rapidly.
Just like erasure, formatting “resets” the entire medium and eliminates all pointers collectively. This uses up more time but handles all of the available storage on the media. Based on the user’s competence and the tools accessible to them, the information can be “un-erased” and retrieved.
2. Overwriting of data
Each bit in data is a binary “0” or “1,” and bits are used to store information. Overwriting modifies the bits to represent newly added data. This sort of phenomenon usually occurs when a user deletes unwanted files and downloads or creates new data on a computer system. This method takes more time since it entails writing over data instead of merely wiping it, but it is more secure than just erasing it.
Moreover, if you don’t erase it completely (often using specialized software), the media may still include pieces of the original data. Even if a diligent bad actor cannot fully recover residual data, they can with enough time and work, put together some data.
3. Degaussing
Degaussing employs a hand-held gadget or larger equipment that generates a strong magnetic field to permanently scramble any data and render the medium useless.
This method works well, however, the medium is where it falls short. Over time, magnetic discs have been replaced by solid-state drives as the primary method of data storage. These drives store data in countless small electronic switches that are not susceptible to degaussing. The same disadvantages apply to erasure, formatting, and overwriting when it comes to SSD data destruction.
4. Physical destruction
The best and safest approach involves not only cleaning procedures but also physically destroying the medium. A specified storage device is broken up, crushed, dissolved, or chopped into tiny pieces. Regardless of whether it was stored on floppy discs, hard drives, thumb drives, or SSDs, data becomes unrecoverable if the device holding it no longer exists, While the media is gone, the protection is well worth the loss since it had sensitive data and outdated hardware.
What to do after Data Destruction?
You must be wondering what to do with your empty hard drives after thoroughly and irreversible wiping all the data from them. Well, we have an answer for you.
E-waste Recycling!
Often after data destruction, hard drives are discarded or disposed of openly, causing harm to the environment. E-waste recycling comes to play a crucial role here. It helps to mitigate environmental damage, conserve resources, and foster a healthier, more sustainable future. Linking e-waste disposal and data destruction showcases a comprehensive approach to the entire lifecycle of electronic drives. Improper E-waste management can have serious consequences on us and nature.
To learn more about it you can check out our blog on Improper E-waste management.
Companies like ours that offer data destruction services also incorporate e-waste recycling services. When individuals are aware that they are handling their data responsibly, they become more inclined to engage in recycling initiatives. Incorporating proper e-waste recycling into data destruction boosts consumer trust.
Data destruction is an integral component of e-waste recycling. It safeguards sensitive information, complies with regulations, and minimizes environmental harm.
What are the benefits of Data Destruction?
Data erasure has a lot of advantages. Whether your primary need is avoiding fines, preventing lost income, or preserving your clients’ trust—they all share one thing in common: peace of mind.
1. Legal Protection
The consequences of a data breach can range from financial losses due to corporate espionage to harsh legal penalties for violating privacy laws. These consequences are determined by the nature of the sensitive information that was compromised. By employing appropriate data management procedures such as destruction and certification, you will be shielded from these liabilities.
2. Breach Protection
Data theft damages a company and is frequently impossible to repair. The majority of impacted businesses cease operations within months following a data breach. Your company’s health and survival depend on maintaining data security and disposing of it properly.
3. Corporate streamlining
Outdated or abandoned hardware not only poses security risks but also takes up a surprisingly large amount of space. A small business that has a room full of outdated equipment or a shelf full of drives is potentially risky. Your firm will run more smoothly by securely saving your data in modernized physical systems or a reliable cloud service and carefully discarding unneeded items.
4. Customer Trust
Businesses, both large and small, constitute a significant portion of the digital landscape. These businesses also bring their clientele and customer bases, along with the necessary data for communication and meeting their requirements. Data security plays a crucial role in maintaining their trust and expanding your business.
Conclusion
It is impossible to overestimate the significance of safe data deletion or the requirement for a reliable provider that provides correct certification.
With the help of our dependable hard drive disposal service and an evaluation of your present information technology, Go Green can make sure that your data destruction and hard drive shredding procedures are protecting your assets and reputation. Contact us to find out how!