Here are a few questions to think about: Do you still watch movies on a VCR player? Absolutely not, I’d say. Do you constantly buy the latest cell phone as it’s released? The answer is definitely yes if you’re like nearly 50% of iPhone users. How many computers have you used during your lifetime? Probably a good number. Have any major home appliances lately undergone an update? Perhaps because research indicates that more individuals than ever are purchasing new appliances. This implies we face an urgent need for proper E-waste management.
But first, we have to know more about what E-waste is and why responsible Electronic waste management is so important.
What is E-waste?
Any electronic product or anything containing electronic components that has reached the end of its functional life cycle is considered electronic garbage, commonly referred to as e-waste. These e waste products contain harmful materials, which many people are unaware of, thus they must be treated carefully when no longer required or needed.
Some of the electronics that we longer need can be used by somebody else .Customers can sell electronic garbage or donate them to someone who might still value them. For customers wishing to upgrade their electronics but want to give up an older model, several businesses also offer trade-in programmes or incentives; the retailers can reuse or repurpose the older models.
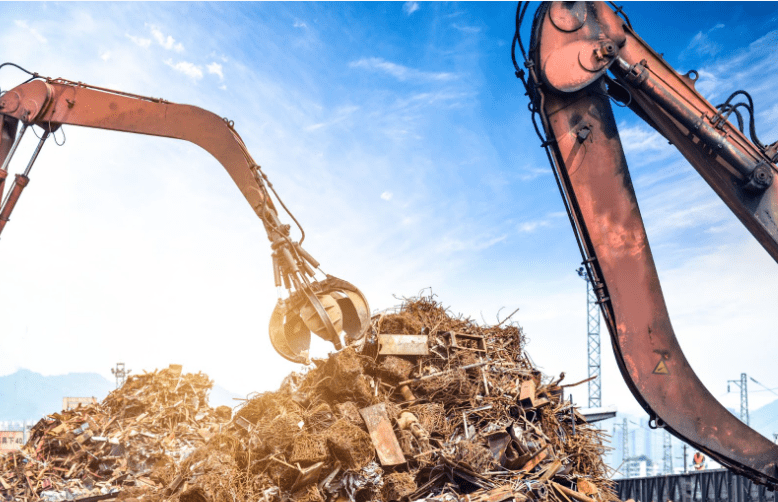
However, if a product is completely useless or broken, it must be recycled, hauled away by a qualified e-waste management service, or brought to a designated drop-off location at a government facility, school, or organization instead of simply being thrown in the trash. This is because e-waste can potentially harm people, pets, and the environment if improperly disposed of.
The effects of inappropriate e-waste collection in landfills or other non-dumping sites pose substantial risks to present public health and have the potential to contaminate ecosystems for future generations. Toxic chemicals are generated when electronics are incorrectly disposed of and wind up in landfills, which has adverse effects on the environment’s air, soil, and water—and ultimately, human health.
In this blog, we will discuss how improper e-waste management affects the environment.
1. Harmful Effect on Air
When e-waste disposal is done informally by disassembling, shredding, or melting the components, dust particles or chemicals, including dioxins, are released into the atmosphere. This causes air pollution and harms respiratory health. Burning is a common practice involved in illegal E-waste management. It is used to extract valuable metals like copper from devices. Burning e-waste increases the chance of developing chronic illnesses and cancer. It releases tiny particles that can travel thousands of kilometers and pose a number of dangers to both human and animal health.
Highly integrated electronics frequently have higher value components like gold and silver. They are removed by using acids, desoldering, and other chemicals. They create toxic fumes in locations where recycling is not well regulated. The people who handle this material are most at risk from the harmful air consequences of informal e-waste management, although the pollution can travel thousands of miles from recycling centers.
Certain animal species are more negatively impacted by e-waste pollution than others. This could put these species and the biodiversity of some heavily contaminated areas in peril. Air pollution over time can harm plant species, soil quality, and water availability, causing irreparable harm to ecosystems.
By extracting precious metals from e-trash, for instance, parties developed an informal recycling hub in Guiyu, China. As a result, the area has exceptionally high lead levels in the air. These chemicals are inhaled and consumed through air, water and soil. In the long run, larger animals, wildlife, and nearby humans can sustain disproportionate neurological damage as a result.
2. Harmful effect on Soil
Both heavy metals and flame retardants can seep directly into the soil during inappropriate E-waste management . This can contaminate nearby or nearby crops, as well as the groundwater beneath them. Heavy metal contamination of the soil makes crops more susceptible to absorbing these toxins. This can lead to a number of ailments and reduce the productivity of the field.
Due to their size and weight, big particles that are liberated during the burning, shredding, or dismantling of e-scrap quickly re-deposit to the ground and contaminate the soil. These pollutants can linger in the soil for a very long time. They affect both plants and soil microbes. In the end, animals and wildlife will eat impacted plants, leading to interior health issues.
3. Harmful Effect on Water
Following soil contamination, heavy metals in e-waste like mercury, lithium, lead, and barium subsequently flow even further through the earth to reach groundwater. These heavy metals eventually find their way into ponds, streams, rivers, and lakes once they enter groundwater. Even if a community is kilometers distant from a recycling site, these channels cause acidification and toxification in the water, making it unhealthy for animals, plants, and communities. Finding clean water to drink becomes difficult.
Freshwater and marine creatures can die from acidification, which can also disrupt biodiversity and damage ecosystems. Acidification can harm ecosystems to the point where recovery is difficult, if not impossible, if it affects water sources.
4. Harmful Effects on Humans
E-waste has toxic chemicals like lithium, barium, lead, cadmium, mercury, and polybrominated flame retardants. Humans exposed to these chemicals can suffer harm to their brain, heart, liver, kidney, and skeletal systems. Additionally, it has a significant impact on the nervous and reproductive systems of humans This can result in illness and birth problems. It is crucial to raise awareness about the hazard posed by improper E-waste management because it poses an incredibly serious risk to the ecosystem worldwide. It is essential to correctly recycle electronic trash so these products can be recycled, refurbished, resold, or reused in order to prevent these hazardous effects of irresponsible e-waste management.
Conclusion
E-waste is a global issue that is getting worse, thus implementation of e-waste management and disposal needs to be stressed more. It has several advantages that far exceed its disadvantages. Manufacturers, consumers, and governments must come up with workable solutions to this pervasive problem. More needs to be done to lessen the harm that e-waste causes, whether it is harmful compounds emitted into the sky or polluted soil entering streams.